SSL certificates are, without a doubt, becoming more and more ubiquitous throughout the web. Not only do they allow you to secure visitors’ connections to your site, but they can also help you rank better in search results. As such, getting an SSL certificate is a no-brainer in most cases.
But when you do get your SSL certificate, you may be surprised to discover that there are actually three different parts to it – the SSL certificate itself, the Intermediate Certificate Authority (CA), and the Private Key. In this article, we will describe how an SSL works and we will focus on the purpose of the Intermediate Certificate Authority.
What Is an SSL Certificate?
SSL, which stands for Secure Sockets Layer, is a popular Digital Certificate. At the heart of every SSL certificate, you will find a set of cryptographic keys. These keys are different on each certificate and they uniquely represent the organization or person for whom the certificate is issued.
What Is the Purpose of an SSL Certificate?
The cryptographic keys in SSL certificates are commonly used to enable HTTPS on websites. Additionally, SSL certificates can confirm the identity of the domain where they are installed, thus preventing phishing attacks. SSL certificates have other uses as well, such as verifying that programs and documents have not been tampered with.
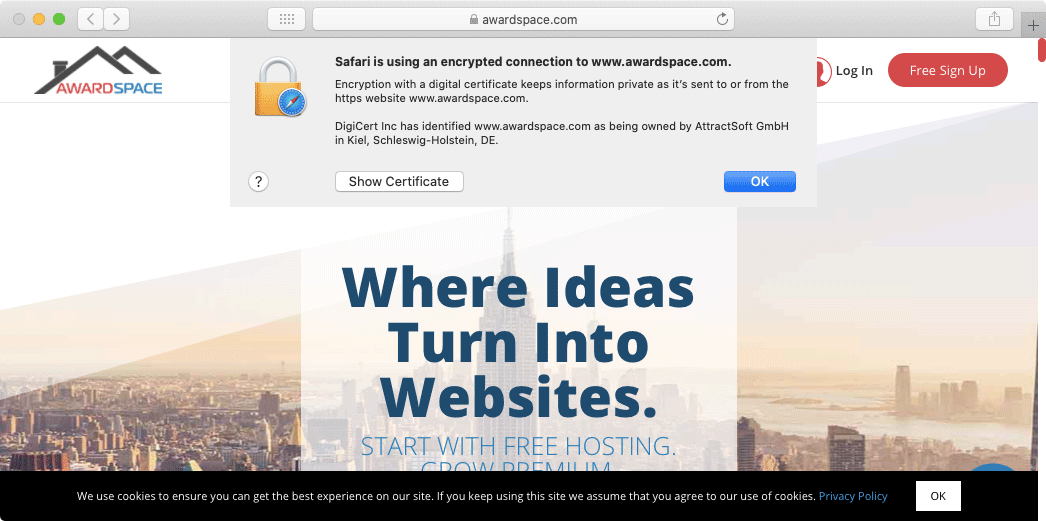
How Do SSL Certificates Work?
Each certificate is created by a trusted Certificate Authority. Before issuing the SSL, the Certificate Authority has the task of verifying the data submitted by the applicant. Once all data is confirmed to be correct and factual, a set of cryptographic keys is generated and the certificate is issued.
An SSL certificate’s security value is derived from two main factors: that the Certificate Authority that has issued the SSL is a trusted one and that the Certificate Authority has performed validity checks before issuing the certificate. As such, when you purchase an SSL certificate and install the SSL on your website, the Certificate Authority effectively vouches for the authenticity of your website.
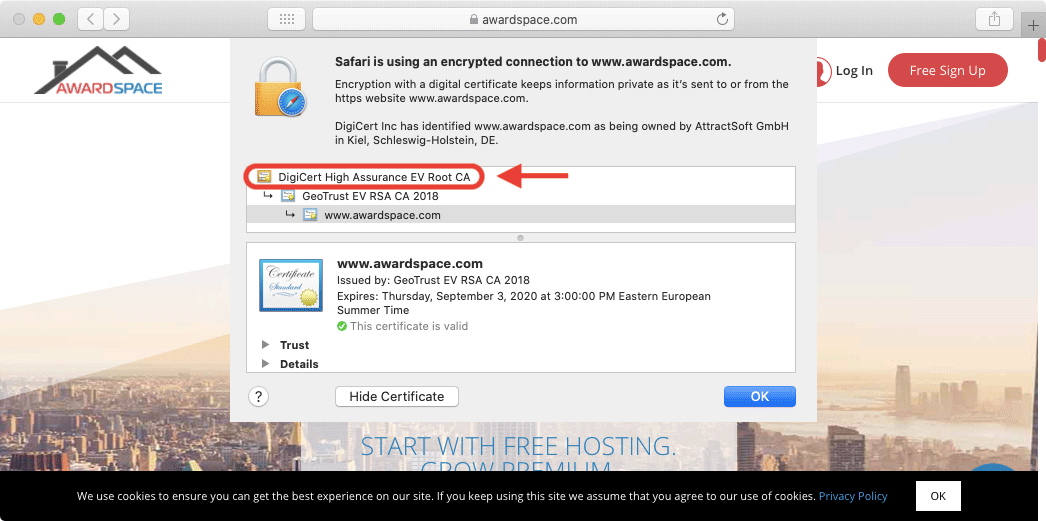
Each Certificate Authority has its own certificate known as a Root CA certificate. This Root CA certificate is used during the creation of your SSL certificate. The Root CA certificates are trusted by most operating systems and web browsers and as such, your SSL certificate is also trusted by extension.
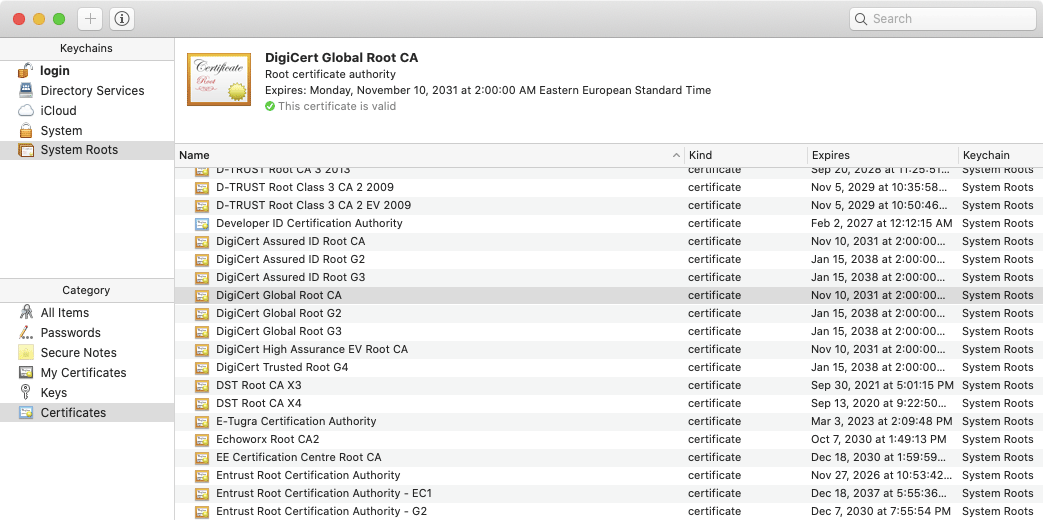
It is actually not common for a Certificate Authority to use its Root CA certificate to issue SSL and other end-user certificates. Instead, an additional layer of certificates is used. These additional certificates are called Intermediate Certificate Authority (CA) certificates.
What Is the Purpose of the Intermediate CA Certificate?
Intermediate CA certificates act as middlemen between the Root CA certificate and the certificates issued to end-users. All three types of certificates create a chain of trust: the web browser implicitly trusts the Root CA certificate, the Root CA certificate trusts the Intermediate CA certificate, and finally, the Intermediate CA certificate trusts the end-user’s SSL certificate.
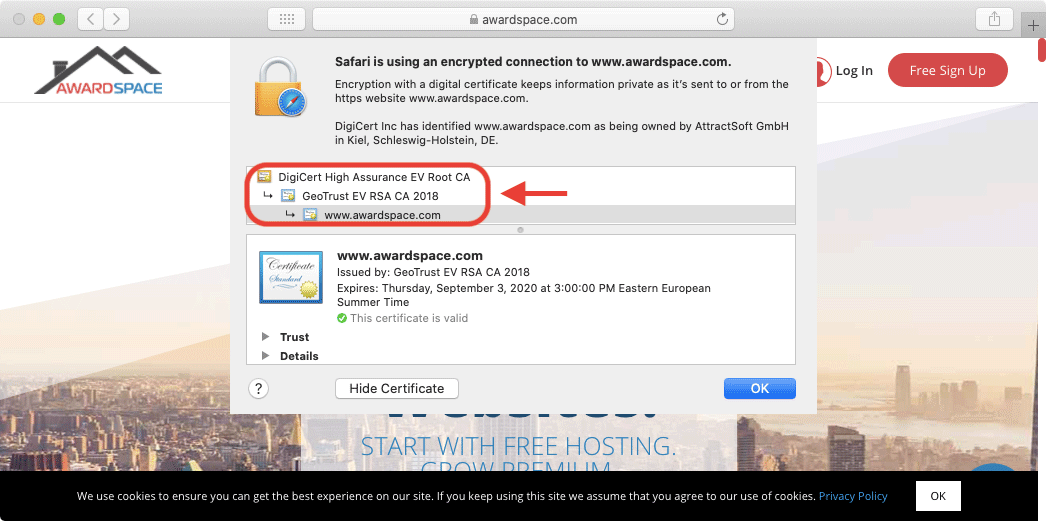
Why Is the Intermediate Certificate Authority Important?
The idea behind the Intermediate CA certificates is to add an extra layer of protection. This higher level of protection is achieved by not having to use the Root CA certificate to issue certificates for end-users. Instead, the Root CA certificate mainly issues Intermediate CA certificates, and these Intermediate CA certificates create SSLs for third-party organizations and individuals.
Is the Intermediate CA Certificate Mandatory?
While it is possible to upload a custom SSL certificate without including the Intermediate CA certificate, it is not recommended. As we have outlined above, the Intermediate CA certificate plays a vital role in the chain of trust between the Root CA certificate and your SSL certificate. By omitting the Intermediate CA certificate, you are breaking this chain of trust.
As a result, most web browsers and operating systems will not be able to recognize that your SSL certificate is coming from a legitimate Certificate Authority. To make matters worse, instead of loading the website, you will likely be presented with a warning message, such as the one shown below:
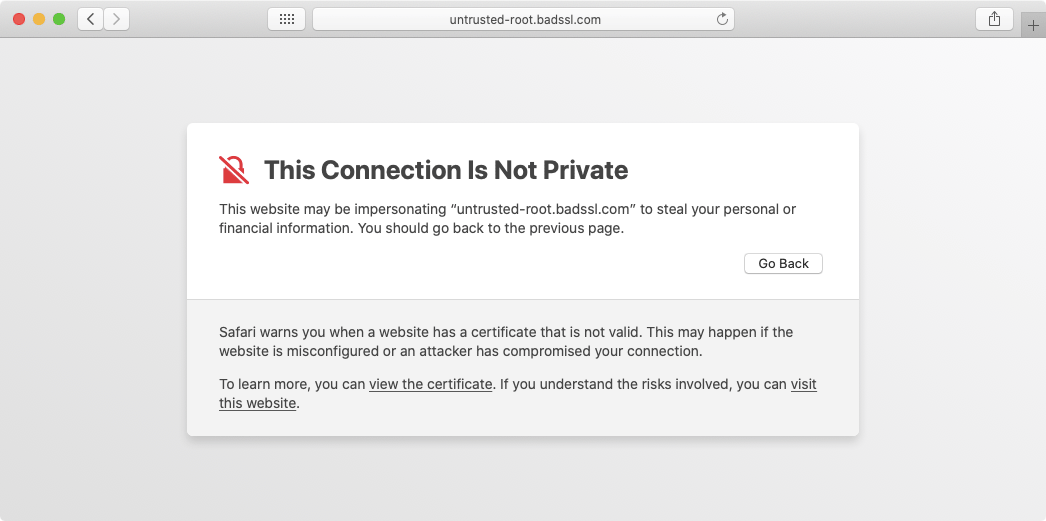
Conclusion
The inclusion of the Intermediate Certificate Authority, although optional, is highly recommended for all website owners. Without the Intermediate Certificate Authority, not all web browsers will recognize the installed SSL certificate as a legitimate one and will display messages discouraging visitors from proceeding to your website.
If you would like to ensure that your SSL is using the Intermediate Certificate Authority, you can contact our 24/7 Technical Support Team for assistance. The only requirements are that you need to be using one of our premium shared hosting plans and that you need to have an active SSL certificate on your domain name.
